|
Нахожу в тесте вопросы, которые в принципе не освещаются в лекции. Нужно гуглить на других ресурсах, чтобы решить тест, или же он всё же должен испытывать знания, полученные в ходе лекции? |
Академия Intel:
Разработка мультимедийных приложений с использованием библиотек OpenCV и IPP
: Литература по курсу
Опубликован: 02.09.2013 | Доступ: свободный | Студентов: 433 / 55 | Длительность: 19:27:00
Тема: Программирование
Специальности: Программист, Системный архитектор
- 1.A threshold selection method from gray-level histogramIEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 9:62-66;1979
- 2.Компьютерное зрениеПер. с англ. — М.: БИНОМ. Лаборатория знаний, 2006.
- 3.Topological Structural Analysis of Digitized Binary Images by Border FollowingCVGIP 30 1, pp 32-46,1985
- 4.Computational Approach to Edge DetectionIEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 8(6), pp. 679-698,1986
- 5.Good Features to Track. Proceedings of the Vision and Pattern RecognitionIEEE Conference on Computer
- 6.Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning.Springer, 2006
- 7.Random Forests // Machine Learning2001. V. 45, №. 1, P. 5–32
- 8.Classification and Regression TreesWadsworth & Brooks, 1984
- 9.Support-Vector Networks // Machine LearningV. 20, № 3. P. 273–297
- 10.A Decision-Theoretic Generalization of Online Learning and an Application to BoostingComputer and System Sciences. Vol.55, . – pp. 119-139. ,1995
- 11.Greedy Function Approximation: a Gradient Boosting MachineTechnical report
- 12.Friedman J. H. Stochastic Gradient Boosting. Technical report. Dept. of Statistics, Stanford
- 13.The Elements of Statistical Learning: Data Mining, InferenceDept. of Statistics, Stanford University, 1999
- 14.Machine LearningMcGraw Hill, 1997
- 15.Some Studies in Machine Learning Using the Game of CheckersIBM Journal. V. 3, University, 1999. № 3. P. 210–229
- 16.Fast algorithms for mining association rules in large databasesProc. 20th Int. Conf. on Very Large Data Bases, VLDB'94, Morgan Kaufmann, 487-499. 1994
- 17.Extensions of dynamic programming as a new tool for decision tree optimizationIn: Ramanna S, Howlett RJ, Jain LC (eds.) Emerging Paradigms in Machine Learning, Springer (to appear). (2011)
- 18.On algorithm for building of optimal ?-decision treesIn: Szczuka MS, Kryszkiewicz M, Ramanna S, Jensen R, Hu Q (eds.) RSCTC 2010. LNCS, vol. 6086:438-445, Springer, Heidelberg. (2010)
- 19.Robust Vehicle Detection through Multidimensional Classification for On Broad Video Based SystemsIEEE. – 2007
- 20.2D Object Detection and Recognition: models, algorithms and networksThe MIT Press, 2002. – 325p
- 21.Support vector machines for multiple-instance learning. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems2002. P. 561-568
- 22.Machine Learning and Robot PerceptionSpringer, 2005
- 23.Robust vehicle detection through multidimensional classification for on board video based systemsICIP, 2008. – pp. 2008-2011
- 24.Detection and tracking of multiple pedestrians in automotive applicationsIntelligent Vehicles Symposium. 2007. – pp. 13-18
- 25.Recognition on an Embedded DSP-PlatformComputer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2007
- 26.Empirical comparison of tree ensemble variable importance measuresChemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems. Vol.105. No.2, 2011. – pp. 157-170
- 27.Computer VisionPrentice Hall Inc., 1982. – 539p
- 28.An Empirical Comparison of Voting Classification Algorithms: Bagging, Boosting, and VariantsMach. Learn. 1999. V. 36, №. 1-2., P. 105-139
- 29.SURF: speed up robust featuresComputer Vision and Image Understanding (CVIU), Vol.110, No.3, 2008. – pp. 346-359
- 30.Pedestrin localization and tracking system with Kalman filtering Intelligent Vehicles Symposium2004. - pp. 584-589
- 31.A modular tracking system for far infrared pedestrian recognitionIntelligent Vehicles Symposium. 2005. – pp. 759-764
- 32.New algorithms for generation decision trees - Ant-Miner and its modificationsFoundations of Computational Intelligence 6:229-262. (2009)
- 33.Image classification using random forests and fernsIn 11th International Conference on Computer Vision, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2007
- 34.Learning OpenCV Computer Vision with OpenCV LibraryO' Reilly Media Publishers, 2008. – 571p
- 35.Random ForestsMach. Learn. 2001. V. 45, №. 1, P. 5-32
- 36.Classification and Regression Trees.Wadsworth & Brooks, 1984
- 37.BRIEF: Binary Robust Independent Elementary Features11th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), 2010
- 38.Algorithm for constructing of decision trees with minimal number of nodesIn: Ziarko W, Yao YY (eds.) RSCTC 2000, Revised Papers. LNCS, vol. 2005:139-143, Springer, Heidelberg. (2001)
- 39.Online learning algorithm for ensemble of decision rulesIn: Kuznetsov SO, \'Sl ezak D, Hepting DH, Mirkin BG (eds.) RSFDGrC 2011. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 6743:310-313, Springer, Heidelberg. (2011)
- 40.Real-time tracking of non-rigid objects using mean shiftIEEE CVPR’2000, Vol.2, 2000. – pp. 142-149
- 41.Histograms of oriented gradients for human detectionComputer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’05), 2005
- 42.Visual categorization with bags of keypointsIn: ECCV International Workshop on Statistical Learning in Computer Vision, 2004
- 43.Hierarchical Semantic Indexing for Large Scale Image RetrievalIEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) – 2011
- 44.What does classifying more than 10,000 image categories tell usProceedings of the 12th European Conference of Computer Vision (ECCV) – 2010
- 45.ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image databaseIn CVPR09. – 2009
- 46.The fastest pedestrian detector in the westMachine Vision. 2010
- 47.Pedestrian Detection: An Evaluation of the State of the ArtPattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (PAMI’11). 2011
- 48.On some new object detection features in OpenCV LibraryPattern Recognition and Image Analysis. 2011. V. 21, № 2. P. 377–379
- 49.Pattern classification (2nd edition).Wiley, 2001
- 50.Monocular Pedestrian Detection: Survey and ExperimentsIEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2009, V. 31, N. 12, P. 2179-2195
- 51.Grant Statistical Methods in Bioinformatics: An Introduction.Springer, 2005
- 52.Fast and robust CAMShift trackingIEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, 2010. – pp. 9-16
- 53.WordNet: An Electronic Lexical Database.MIT Press, 1998
- 54.Object Detection with Discriminatively Trained Part Based ModelsIEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence. 2010. Vol.32, No.9. – pp. 1627–1645
- 55.Cascade object detection with deformable path modelComputer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR'10). 2010
- 56.(2010) UCI Machine Learning Repository
- 57.Real-time stereo vision for urban traffic scene understandingIntelligent Vehicles Symposium. 2000. – pp. 273-278
- 58.The design and use of steerable filtersIEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, Vol.13, No.9, 1991. – pp. 891-906
- 59.A decision-theoretic generalization of online learning and an application to boostingComputer and System Sciences. Vol.55, 1997. – pp. 119-139
- 60.Greedy function approximation: the gradient boosting machineAnnals of Statistics. 2001. V. 29, N. 5. P. 1189-1232
- 61.Greedy Function Approximation: a Gradient Boosting Machine.Technical report. Dept. of Statistics, Stanford University, 1999
- 62.Stochastic Gradient Boosting.Technical report. Dept. of Statistics, Stanford University, 1999
- 63.Importance Sampled Learning EnsemblesTechnical report. Dept. of Statistics, Stanford University
- 64.Vision-based pedestrian detection: the protector systemProceedings of the IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, Parma, Italy. – 2004. – pp. 13-18
- 65.Pedestrian detection from a moving vehicleComputer Vision. Vol.2. 2000. – pp. 37-49
- 66.Pyramid match kernels: Discriminative classification with sets of image featuresIn Proc. ICCV, 2005
- 67.Pyramid match kernels: Discriminative classification with sets of image featuresIn Proc. ICCV, 2005
- 68.3D vision sensing for improved pedestrian safety Intelligent Vehicles Symposium.2004. – pp. 19-24
- 69.The Minimum Description Length Principle. Foreword by Jorma Rissanen. Adaptive Computation and Machine Learning.MIT Press
- 70.The Elements of Statistical Learning: Data Mining, Inference, and PredictionSpringer, 2001
- 71.Pyramidal Image Analysis for Vehicle DetectionProceedings to Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, 2005. – pp. 88-93
- 72.Robust Extraction of Wheel Region for Vehicle Position Estimation using a Circular Fisheye CameraInternational Journal of Computer Science and Network Security, Vol.9
- 73.Determing Optical FlowMIT Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, №572. – 1980
- 74.Semantics-preserving dimensionality reduction: rough and fuzzy-rough-based approachesIEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering 16:1457-1471
- 75.Real-time tracking and outlier rejection with changes in illuminationICCV’01, Vol.1, 2001. – pp. 684-689
- 76.Speech and Language Processing: An Introduction to Natural Language Processing, Computational Linguistics and Speech Recognition. Second EditionPrentice Hall, 2008
- 77.Forward-backward error: automatic detection of tracking failuresICPR’10, 2010. – pp. 2756-2759
- 78.Vehicle Segmentation and Tracking from a Low-Angle Off-Axis CameraProceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), San Diego, California, June 2005. – 2005
- 79.PCA-SIFT: A more distinctive representation for local image descriptorsComputer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’04), Vol.2, 2004. – pp. 506-513
- 80.Saul Distance Metric Learning for Large Margin Nearest Neighbor ClassificationJMLR. 2009 V. 10 P. 207-244
- 81.Wavelet-based Vehicle Tracking for Automatic Traffic SurveillanceIEEE Catalogue No.01CH37239. – 2001
- 82.Beyond bags of features: Spatial pyramid matching for recognizing natural scene categoriesIn: CVPR, 2006
- 83.Real-time pedestrian and vehicle detection in video using 3D cuesICME’09 Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE international conference on Multimedia and Expo. – 2009. – pp. 614-617
- 84.Dynamic 3D scene analysis from a moving vehicleComputer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’07). 2007. – pp. 1-8
- 85.Robust Object Detection with Interleaved Object Categoization and SegmentationSpringler Science + Business Media, LLC. – 2007
- 86.Measuring the semantic relatedness between words and imagesInternational Conference on Computational Semantics (IWCS) – 2011.
- 87.Classification rule discovery with ant colony optimizationIn: Proc. IEEE/WIC Int. Conf. on Intelligent Agent Technology, IAT 2003, IEEE Computer Society, Washington, DC, 83-88
- 88.Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypointsIJCV 60, P. 91–110, 2004
- 89.An iterative image registration technique with an application to stereo visionIJCAI’81, Vol.2, 1981. – pp. 674-679
- 90.Robust wide baseline stereo from maximally stable extremal regionsBritish Machine Learning Conference, 2002. – pp. 384-393
- 91.iAQ: A program that discovers rules, AAAI-07 AI Video CompetitionIn: 22nd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. (2007)
- 92.Performance Evaluation of Local DescriptorsIEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, Vol.27, No.10, 2005. – pp. 1615-1630
- 93.Scale and affine invariant interest point detectorsInternational Journal of Computer Vision, 60(1), 2004. – pp. 63-86
- 94.Machine Learning.McGraw-Hill Science/Engineering/Math, 1997
- 95.On algorithm for constructing of decision trees with minimal depth. Fundamenta Informaticae41:295-299.(2000)
- 96.Partial Covers, Reducts and Decision Rules in Rough Sets: Theory and ApplicationsStudies in Computational Intelligence, vol. 145. Springer, Heidelberg. (2008)
- 97.Combinatorial Machine Learning: A Rough Set Approach.Studies in Computational Intelligence, vol. 360. Springer, Heidelberg.(2011)
- 98.An experimental study on pedestrian classificationIEEE Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (PAMI’06).Vol.28, No.11, 2006. pp. 1863-1868
- 99.Exploiting Hierarchical Contex on a large database of object categoriesIEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’10). 2010. – pp. 129-136
- 100.Efficient Non-Maximum SupressionInternational Conference on Pattern Recognition, 2006. – pp. 850-855
- 101.Approximate Boolean reasoning: foundations and applications in data miningIn: Peters JF, Skowron A (eds.), Transactions on Rough Sets V. LNCS, vol. 4100:334-506, Springer, Heidelberg. (2006)
- 102.PLANET: Massively parallel learning of tree ensembles with MapReduce.Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Very Large Data Base (VLDB). 2009. P. 1426-1437
- 103.Multiple instance boost using graph embedding based decision stump for pedestrian detectionComputer Vision. Vol.4, 2008. - pp. 541-552
- 104.A trainable system for object detectionComputer Vision. Vol.38. No.1, 2000. – pp. 15-33
- 105.Rough Sets – Theoretical Aspects of Reasoning about DataKluwer Academic Publishers
- 106.Rough sets and Boolean reasoningInformation Sciences 177: 41-73. (2007)
- 107.Recognition for Smart EnvironmentsIEEE Computer Vision. – 2000. – pp. 50-55
- 108.Induction of decision treesMachine Learning 1, 1986. – pp. 81-106
- 109.C4.5: Programs for Machine Learning,Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, San Mateo. (1993)
- 110.Modeling by shortest data description.Automatica 14:465-471. (1978)
- 111.Machine Learning for high-speed corner detection9th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV 2006), 2006. – pp. 430-443
- 112.Detecting pedestrians by learning shapelet featuresComputer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’07). 2007
- 113.The boosting approach to machine learningAn overview MSRI workshop on Nonlinear Estimation and Classification. Springer, 2002
- 114.Good features to trackIEEE, 1994. – pp. 593-600
- 115.Contour-based Learning for Object Detection10th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV’05). 2005. Vol.1. – P. 503-510
- 116.Rough sets in KDDIn: Shi Z, Faltings B, Musem M. (eds.) 16th World Computer Congress. Proc. Conf. Intelligent Information Processing, 1-17. Publishing House of Electronic Industry, Beijing. (2000)
- 117.The discernibility matrices and functions in information systemsIn: Slowinski R (ed.) Intelligent Decision Support. Handbook of Applications and Advances of the Rough Set Theory, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, 331-362. (1992)
- 118.Order-based genetic algorithms for the search of approximate entropy reducts.In: Wang G, Liu Q, Yao Y, Skowron A (eds.) Proc. 9th Int. Conf. Rough Sets, Fuzzy Sets, Data Mining, and Granular Computing, RSFDGrC 2003. LNAI, vol. 2639:308-311, Springer, Heidelberg. (2003)
- 119.Image Processing, Analysis and Machine Vision.Thomson, 2008. – 866p
- 120.Computer Vision: Algorithms and Applications.Springler, 2010. – 979p
- 121.Robust Vehicle Detection for Tracking in Highway Surveillance Videos using unsupervised LearningAdvanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance (AVSS '09), 2009. – pp.529-534
- 122.A Fast Local Descriptor for Dense MatchingIEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’08), 2008. – pp. 1-8
- 123.Contex-based Vision System for Place and Object Recognition9th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV’03). 2003. Vol.1. – pp. 273-283
- 124.Local Invariant Feature Detectors: A SurveyFoundation and Trends in Computer Vision, Vol.3, No. 3, 2007. – pp. 177-280
- 125.Parallel boosted regression trees for web search ranking.Proceedings of the 20th international conference on World wide web. 2011. P. 387-396
- 126.Vehicle Tracking Using a Human-Vision-Based Model of Visual SimilarityIEEE. – 2010
- 127.Detecting pedestrians using patterns of motion and appearanceComputer Vision. Vol.63. No.2, 2005. – pp. 153-161
- 128.Rapid object detection using a boosted cascade of simple featuresIn Proceedings IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. – 2001
- 129.Robust Real-Time Face Detectioninternational Journal of Computer Vision 57(2). – 2004. – pp. 137-154
- 130.Detecting pedestrians using patterns of motion and appearanceIn: Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Vol. 1 – 2003. – pp. 734-741
- 131.New features and insights for pedestrian detectionComputer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR'10). 2010
- 132.Statistical and Inductive Inference by Minimum Message Length.Information Science and Statistics. Springer, New York. (2005)
- 133.A performance evaluation of single and multi-feature people detectionDAGM-Symposium. 2008. – pp.82-91
- 134.Multi-cue onboard pedestrian detectionComputer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR'09). 2009. – pp. 794 - 801
- 135.Finding minimal reducts using genetic algorithm.In: Proc. 2nd Annual Join Conf. on Information Sciences, Wrightsville Beach, NC, 186-189. (1995)
- 136.Detection and tracking of multiple, partially occluded humans by bayesian combination of edgelet based part detectorsComputer Vision. Vol.75. No.2, 2007. – pp. 247-266
- 137.Logistic regression and boosting for labeled bags of instancesKnowledge Discovery and Data Mining (KDDM’04), 2004
- 138.High Performance Data Mining: Scaling Algorithms, Applications and SystemsKluwer Academic Publishers, 1999
- 139.Pedestrian detection in infrared images based on local shape featuresComputer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’07). 2007
- 140.On-road vehicle detection using Gabor filters and support vector machinesDigital Signal Processing,Vol.2, 2002.- pp. 1019-1022
- 141.Fast Human Detection Using a Cascade of Histograms of Oriented GradientsComputer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’06). Vol.2, 2006. – pp. 1491-1498
- 142.Optimization of decision rules based on methods of dynamic programmingVestnik of Lobachevsky State University of Nizhni Novgorod 6:195-200 (in Russian) (2010)
- 143.Теория распознавания образов. Статистические проблемы обучения.М.: Наука, 1974
- 144.Параллельная реализация алгоритма предсказания с помощью модели градиентного бустинга деревьев решенийВестник Южно-Уральского государственного университета. Серия: Математическое моделирование и программирование. 2011. No. 37 (254). С. 82-89
- 145.Программная реализация алгоритма градиентного бустинга деревьев решений.Вестник ННГУ, вып. 1, 2011. С. 193-200
- 146.Новые математические подходы к задачам медицинской диагностики.М.: УРСС, 2004
- 147.Компьютерное зрение. Современный подходМ.: Изд. д. Вильямс, 2004. – 465с
- 148.Data Mining: учебное пособиеМ.: Интернет-университет информационных технологий: БИНОМ: Лаборатория знаний, 2006
- 149.A sparse object category model for efficient learning and exhaustive recognitionIn IEEE Computer Society Conference onComputer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’2005), pp. 380–387, San Diego, CA (2005)
- 150.Object Class Recognition by Unsupervised Scale-Invariant LearningIn Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2003, V.2, pp. 264-271
- 151.Spatial priors for part-based recognition using statistical models.In IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’2005), pp. 10–17, San Diego, CA. (2005)
- 152.Pictorial structures for object recognition.International Journal of Computer Vision, 61(1):55–79. (2005)
- 153.Visual categorization with bags of keypointsIn ECCV International Workshop on Statistical Learning in Computer Vision, Prague (2004)
- 154.Hierarchical part-based visual object categorizationIn IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’2005), pp. 709–714, San Diego, CA.(2005)
- 155.Sparse flexible models of local featuresIn Ninth European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV 2006), pp. 29–43 (2006)
- 156.Pattern Recognition and Machine LearningSpringer, New York, NY
- 157.The representation and matching of pictorial structuresIEEE Transactions on Computers, 22(1):67–92
- 158.Discriminative Object Class Models of Appearance and Shape by CorrelatonsIn Proc. IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New York, 2006
- 159.A hierarchical model of shape and appearance for human action classificationIn: Proc. CVPR (2007)
- 166.
- 167.
- 169.
- 170.
- 172.Компьютерное зрение.М.: Бином. Лаборатория знаний, 2006. 752с
- 173.In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 1998. V. 2
- 174.Background Modeling using Mixture of Gaussians for Foreground Detection -A Survey Recent Patents on Computer Science 1, 3. 2008. P. 219-237
- 175.Maximum Likelihood from Incomplete Data via the EM AlgorithmJournal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series B (Methodological), Vol. 39, No. 1. (1977), pp. 1-38
- 176.Computer Vision: Algorithms and Applications.Springler, 2010. 979p
- 177.Компьютерное зрение. Современный подход.М.: Изд. д. Вильямс, 2004. 465с
- 178.Preemptive RANSAC for live structure and motion estimationIn the Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision 2003 (ICCV’03). 2003. P.199-206
- 179.Learning OpenCV Computer Vision with OpenCVLibrary. O' Reilly Media Publishers, 2008. 571p
- 180.Image Processing, Analysis and MachineVision. Thomson. 2008. 866p
- 181.Detection with Interleaved Object Categoization and Segmentation.Springler Science + Business Media, LLC, 2007
- 182.Real-time pedestrian and vehicle detection in video using 3D cuesIn Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE international conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME’09). 2009. P. 614-617
- 183.Auniversal background subtraction algorithm for video sequencesIEEE Transactions on Image Processing. 20(6).2011. P.1709-1724
- 184.Determing Optical FlowMIT Artificial Intelligence Laboratory. 1980. №572
- 185.IEEE Transactions on Image Processing. 1994. 3(5). P. 625–638
- 186.Learning Layered Motion Segmentations of VideoIn International Journal of Computer Vision (IJCV). 2008. V.76, №3, P. 311-319
- 187.Object tracking: A surveyACM Computing Surveys. 2006. V. 38. № 4, Article 13
- 188.Resolving motion correspondence for densely moving points.IEEE Trans. Pattern Analysis Machine Intelligence. 2001. V.23. № 1. P. 54-72
- 189.Vehicle tracking using Kalman filter and featuresSignal & Image Processing: An International Journal (SIPIJ). 2011. V.2, №2
- 190.Algorithm Based on SIFT and Kalman FilterIn Proceedings The 2nd International Conference on Computer Application and System Modeling. 2012. – P.1563-1566
- 191.Corner feature based object tracking using Adaptive Kalman FilterIn Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Signal Processing (ICSP 2008). 2008. P. 1432-1435
- 192.Condensation - conditional density propagation for visual trackingInt. J. Comput. Vision. 1998. V.29. № 1. P. 5-28
- 193.Particle Filters for Positioning, Navigation and TrackingIEEE Transactions on Signal Processing. 2002. V.2. Issue 2. P. 425-437
- 194.Real-time tracking of non-rigid objects using mean shiftIn Proceedings of the CVPR’00. 2000. V.2, P. 142-149
- 195.Fast and robust CAMShift trackingIn Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. 2010. P. 9-16
- 196.Determining optical flowMIT, Artificial Intelligence Laboratory. 1980
- 197.Good features to trackIEEE. 1994. P. 593-600
- 198.Real-time tracking and outlier rejection with changes in illuminationIn Proceedings of the ICCV’01. 2001. V.1. P. 684
- 199.Performance of optical flow techniquesInternational Journal of Computer Vision. 1994. V.12. № 1. P.43-77
- 200.The elements of statistical learningData mining, inference and prediction. 2001. 745p
- 201.Быстрое преобразование Фурье и алгоритмы вычисления свертокМ.: «Радио и связь». 1985. 247с
- 202.Матричные вычисленияМ.: Изд-во «Мир». 1999. 548с
- 203.
- 207.Multiple View Geometry in ComputerCambridge University Press, 2004
- 213.
- 218.Learning OpenCV.O’Reilly, 2008. – 571p
- 235.Real-Time Face Detectioninternational Journal of Computer Vision 57(2). – 2004. – pp. 137-154
- 236.Object Detection with Discriminatively Trained Part Based ModelsIEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence. 2010. Vol.32, No.9. – pp. 1627–1645
- 237.Компьютерное зрение. Современный подходМ.: Изд. д. Вильямс, 2004. – 465с. 21. Suzuki S., Abe K. Topological Structural Analysis of Digitized Binary Images by Border Following CVGIP 30 1. – 1985. – pp. 32-46
- 238.Компьютерное зрениеМ.: Бином. Лаборатория знаний, 2006. – 752с
- 239.On the detection of dominant points on digital curvesIEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence. – Vol. II No. 8. – 1989. – pp. 859-872
- 240.Learning OpenCV Computer Vision with OpenCV LibraryO' Reilly Media Publishers, 2008. 571p
- 241.Компьютерное зрение.М.: Бином. Лаборатория знаний, 2006. 752с
- 242.Компьютерное зрение. Современный подходМ.:Изд. д. Вильямс, 2004. 465с
- 243.A computational approach to edge detectionIEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence. Vol. PAMI-8. No.6. 1986. P.679-698
- 248.
- 252.The Elements of Statistical LearningData Mining, Inference, and Prediction. Springer, 2001
- 253.Classification and Regression TreesWadsworth & Brooks, 1984
- 254.New object detection features in the OpenCV LibraryPattern Recognition and Image Analysis. 2011. V. 21, № 3. P. 384–386
- 255.Feature detection with automatic scale selectionInternational Journal of Computer Vision. 1998. V.30. Issue
- 256.Random ForestsMachine Learning 2001. V. 45, № 1. P. 5–32
- 257.k-means++: the advantages of careful seedingProceedings of the eighteenth annual ACM-SIAM symposium on Discrete algorithms. 2007. P. 1027–1035
- 258.М.: Издательство Московского университета, 2010. –272 с., ил. – (Серия «Супер-компьютерное образование»)
- 259.IntelPress, 2004
- 260.Censure: Center surround extremas for realtime feature detection and matchingIn European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV 2008), pp. 102–115
- 261.SURF: speed up robust featuresComputer Vision and Image Understanding (CVIU). 2008. V.110, № 3. P. 346-359
- 262.Learning OpenCV Computer Vision with OpenCVLibrary. O' Reilly Media Publishers, 2008. 571p
- 263.In Proceedings of the 11th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV’10). 2010
- 264.Learning for high-speed corner detectionIn Proceedings of the 9th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV’06). 2006. P. 430-443
- 265.Springer, 2008
- 266.PCA-SIFT: A more distinctive representation for local image descriptorsIn Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’04). 2004. V.2. P. 506-513
- 267.International Journal of Computer Vision. 2004. № 60. P. 91–110
- 268.British Machine Learning Conference. 2002. P. 384-393
- 269.International Journal of Computer Vision. 2004. № 60(1). P. 63-86
- 270.In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision (CVPR’11). 2011. P. 2564-2571
- 271.Springler, 2010. 979p
- 273.М.: Изд. д. Вильямс, 2004. – 465с
- 274.Springler, 2010
- 278.Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). 2005. V. 1. P. 886-893
- 279.документации OpenCVPattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence. 2009. V. 31, № 12. P. 2179-2195
- 280.Компьютерное зрениеМ.: Бином. Лаборатория знаний. 2006. 752с
- 281.Image Processing, Analysis and Machine VisionThomson. 2008. 866p
- 282.Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis. 2011. V. 21, № 3. P. 384–386
- 286.in IEEE Conf. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2009
- 287.in British Machine Vision Conf., 2005
- 288.CVPR, Fort Collins, Colorado, USA, pages 87-93, 1999
- 290.М.: МЦНМО, 2001
- 291.J. Symbolic Computation, 9(3). – P. 251–280, 1990
- 293.
- 295.СПб.: Питер, 2007
- 296.Morgan Kaufmann, 2006
- 297.М.: Изд. д. Вильямс, 2004. – 465с
- 298.Computer Vision: Algorithms and ApplicationsSpringer, 2010
- 299.Rapid object detection using a boosted cascade of simple featuresIn: Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Kauai, Hawaii, USA, Vol. 1, 2001, pp. 511-518
- 300.International Journal of Computer Vision. 2004. № 60. P. 91–110
- 301.British Machine Learning Conference. 2002. P. 384-393
- 302.International Journal of Computer Vision. 2004. № 60(1). P. 63-86
- 303.In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision (CVPR’11). 2011. P. 2564-2571
- 304.Springler, 2010. 979p
- 306.М.: Изд. д. Вильямс, 2004. – 465с
- 307.Springler, 2010
- 308.Intel® Corporation, 2007
- 309.Материалы образовательного комплекса «Параллельные численные методы». – Нижний Новгород, 2010
- 310.Object Detection with Discriminatively Trained Part Based ModelsIEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence. 2010. Vol.32, No.9. – P. 1627–1645
- 311.Intel® Threading Building Blocks. Tutorial. Version 1.6Intel® Corporation, 2007
- 312.Библиотека Intel Threading Building Blocks – краткое описание. Материалы образовательного комплекса «Технологии разработки параллельных программ».Нижний Новгород (2007)
- 313.М.: Издательство Московского университета, 2010. –272 с., ил. – (Серия «Супер-компьютерное образование»)
- 314.IntelPress, 2004
- 315.The Software Optimization Cookbook. High-Performance Recipes for the Intel® ArchitectureIntel Press, 2006
- 316.Техника оптимизации программ. Эффективное использование памятиBHV, 2003
- 317.On some new object detection features in OpenCV LibraryPattern Recognition and Image Analysis.2011. V. 21, № 2. P. 377–379
- 318.In Proceedings of the 11th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV’10). 2010
- 320.
- 323.М.: МЦНМО, 2001
- 324.J. Symbolic Computation, 9(3). – P. 251–280, 1990
- 325.BHV, 2003
- 326.Intel Press, 2006
- 327.IntelPress, 2004
- 328.СПб.: Питер, 2007
- 329.Morgan Kaufmann, 2006
- 330.CVPR, Fort Collins, Colorado, USA, pages 87-93, 1999
- 331.in British Machine Vision Conf., 2005
- 332.in IEEE Conf. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2009
- 333.Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). 2005. V. 1. P. 886-893
- 334.Monocular Pedestrian Detection: Survey and ExperimentsPattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence. 2009. V. 31, № 12. P. 2179-2195
- 335.An Evaluation of the State of the ArtPattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence. 2012. V. 34, № 4. P. 743-761
- 336.Image Processing, Analysis and Machine VisionPattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence. 2010. V. 32, № .9. P. 1627-1645.
- 337.Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis. 2011. V. 21, № 3. P. 384–386
- 338.
- 340.
- 341.М.: Изд. д. Вильямс, 2004. – 465с

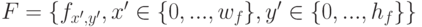 "
"