Optimizing compiler. Vectorization
The presentation can be downloaded here.
Different kinds of parallel:
An optimizing compiler is a tool which translates source code into an executable module and optimize source code for better performance. Parallelization is a transformation of the sequential program into multi-threaded or vectorized (or both) to utilize multiple execution units simultaneously without breaking the correctness of the program.
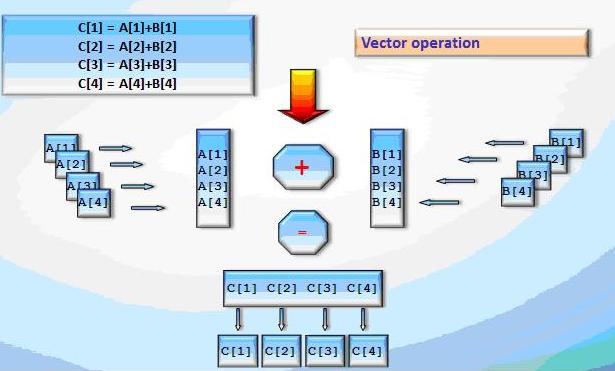
A typical vector instruction is an operation on two vectors in memory or in fixed length registers. These vectors can be loaded from memory by a single or multiple operations.
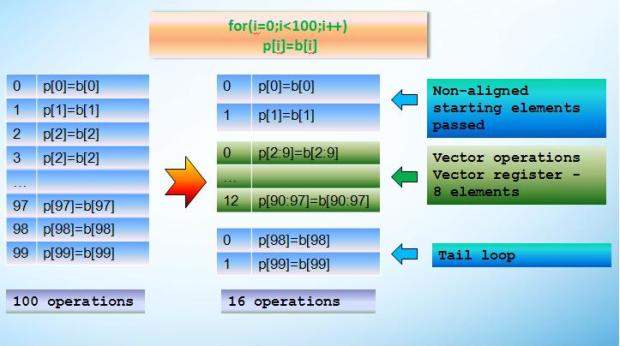
Vectorization is a compiler optimization that inserts vector instructions instead of scalar. This optimization "wraps" the data into vector; scalar operations are replaced by operations with these vectors (packets).
Such optimization can be also performed manually by developer.
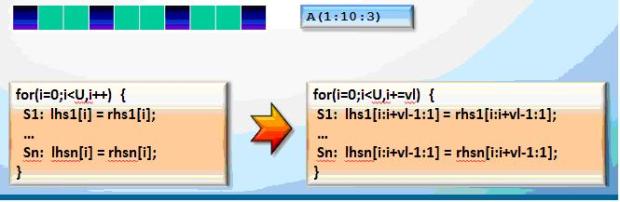
A (1: n: k) - section of the array in Fortran is very convenient for vector register representation.
MMX, SSE vector instruction sets
MMX is a single instruction, multiple data (SIMD) instruction set designed by Intel, introduced in 1996 for P5-based Pentium line of microprocessors, known as "Pentium with MMX Technology".
MMX (Multimedia Extensions) is a set of instructions perform specific actions for streaming audio/video encoding and decoding.
- MMM0-MMM7 64 bit registers (were aliased with existing 80 bit FP stack registers)
- the concept of packages (each register can store one 64 bit integer or 2 - 32 bit or 4 - 16 bit or 8 - 8-bit)
- 57 instructions are divided into groups: data movement, arithmetic, comparison, conversion, logical, shift, shufle, unpack, cache control and prefetch state management.
MMX provides only integer operations. Simultaneous operations with floats and packed integers are not possible.
Streaming SIMD Extensions (SSE) is a SIMD instruction set extension of the x86 architecture, designed by Intel and introduced with Pentium III series processors in 1999. SIMD instructions can greatly increase the performance when exactly the same operations are performed on the multiple data objects. Typical applications are digital signal processing and computer graphics.
- 8 128-bit registers (xmm0 to xmm7)
- set of instructions for operations with scalar and packed data types
- 70 new instructions for single precision floating point data mainly
SSE2, SSE3, SSEE3, SSE4 are further extensions of SSE.
SSE2 has packed data type with double precision floating point.
Advanced Vector Extensions (AVX) is an extension of the x86 instruction set architecture for Intel and AMD microprocessors proposed by Intel in March 2008. Firstly supported by Intel Westmere processor in Q1 2011 and by AMD Bulldozer processor in Q3 2011.
AVX provides new features, new instructions and a new coding scheme.
The size of vector registers is increased from 128 to 256 bits (YMM0-YMM15).
The existing 128-bit instructions use the lower half of YMM registers.