Optimizing compiler Scalar optimizations
SSA (Static single assignment form)
SSA form proposes unique name for each variable definition and introduction of special pseudo-assignments.
SSA is designed to save developers from building complex use / def chains for local variables. Power of SSA is that each variable has only one definition in the program. Therefore, use / def chain is trivial.
SSA introduces special presentation of Phi-functions in places with uncertainty, to create a new variable. This so-called pseudo-assignment. In the construction is necessary to place Phi - functions and create new unique variables.
The new variables are generated by completing the variable name with a unique option. In order to correctly insert the Phi function is necessary to consider some of the concepts of graph theory.
Node N dominates node M if all ways to M pass through N. A node is an immediate dominator of node M if it is the last dominator on any path from entry node to M.
Dominance frontier of node x is set w of all nodes where x dominates all predecessors nodes from w, but doesn’t dominates nodes from w.
Dom[5] = {5,6,7,8}
DF[5] ={5,4,12,11}
In SSA form, each variable definition must dominate the use of this variable.
Construction of the dominators set for each basic block can be the following:
The set of dominators for a node N is the intersection of the dominators set of all his predecessors, and the node itself.
Strict dominator N, this dominator!= N. Immediate dominator – the closest node from the set of dominators.
idom (N) - the immediate dominator for basic block N
children (N) - the set of basic blocks for N, which it dominates
Criterion of dominance frontier: if the basic block N contains a definition of variable A, then every node on the dominance frontier of node N requires Phi function for A. Each Phi function is also the definition, so you must apply the criterion while there are nodes which requires Phi function.
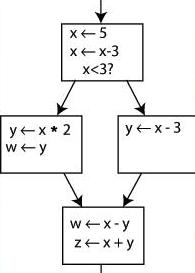
Inserting ? functions for the node 5 of the scheme on slide 25
Optimization using the SSA form:
-
Dead code elimination
- If the variable a_ver is not used than it should be removed.
-
Constant propagation
- If there is an assignment a_ver = const, then all of a_ver should be replaced by const
- If there is a Phi-function a_next = Phi (c, c) than Phi should be replaced by c.
- Copy propagation
- If there is an assignment a_n = b_k than all usages of a_n should be replaced with b_k.
- If there is an assignment a_n = Phi (b_k, b_k) than Phi should be replaced with b_k.